What is a high quality steam drum fertilizer granulator?
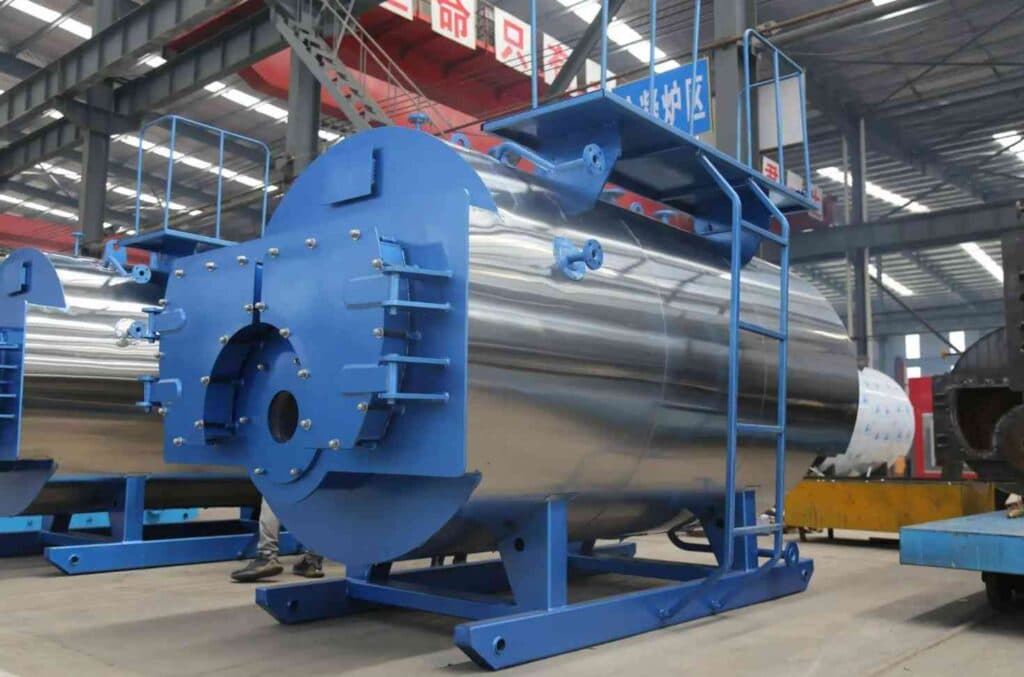

Steam drum granulation represents a prominent technique within the compound fertilizer industry, offering a novel approach to generating high-quality compound fertilizers compared to traditional methods. This method relies on the utilization of a rotary drum fertilizer granulator and a steam boiler. Its key advantage lies in its ability to produce uniform, spherical granules with consistent properties. Central to the steam drum granulation process is the pivotal role of ammonia, which directly influences the quality of the resultant compound fertilizer. So in this article we are going to explain what are the important aspect of steam drum method fertilizer granulator and how it is made of high quality.
What is steam drum granulation method for organic and npk fertilizer?
Steam drum granulation is a method for producing NPK compound fertilizer, utilizing ammonia, typically favored for creating urea-based fertilizer known for its capacity to form round granules. The quantity of steam required can fluctuate depending on the specific process flow and desired product specifications. Thus, when selecting the appropriate steam boiler, it’s crucial to seek guidance from fertilizer experts like TONGLI to ensure the selection of the correct boiler model.
What are the types of steam fertilizer granulator?
A granulator is a chemical equipment used to turn powdery materials into pellets or granules. Its main raw materials are powdery materials, such as fertilizer, cement, dry lime, etc. The working principle of the granulator is to mix powdery materials with binders and then make them into granules through the action of external force. There are generally two types of binders for granulators, one is dry binder and the other is wet binder. Adding water, adding oil and adding steam are all wet processing methods.
What is the process flow and working principle of fertilizer granualtion?
During the granulation process, adding water, oil and steam can improve the granulation quality by providing humidity and adhesion to the material. Among them, adding steam is a common method. Adding steam has three main functions:
1. Granulation efficiency improvement
- First, it improves granulation efficiency. After the material is stimulated by steam, the humidity increases, which can improve the flow characteristics of the material, reduce the resistance during granulation, and improve the granulation efficiency.
2. Granulation quality improvement
- The second is to improve the granulation quality. By heating the steam, the binder in the material can penetrate into the material more evenly, and the material particles can be more closely combined to improve the granulation quality.
3. Save energy consumption
- The third is to save energy consumption. Heating steam can increase the material temperature, thereby reducing energy consumption during the granulation process and achieving energy saving effects.
How much steam is needed for granulation of NPK fertilizers?
The quantity of steam required for granulating NPK fertilizer is not fixed; it depends on the scale of the production line. Steam is utilized to blend the raw materials in the rotary granulator, providing both heat and necessary moisture for agglomeration. The amount of steam used can vary based on the desired granule size and composition. For instance, in a TONGLI 150,000 tons per year 15-15-15 NPK compound fertilizer production line, a steam boiler of 4T per hour is equipped, meaning 4 tons of steam is required every hour to produce 15 tons of NPK compound fertilizer. However, upgrading to a 6T per hour steam boiler is recommended if the budget allows, as it can increase the production output beyond the nominal design capacity.
What you should know before purchasing the steam boiler for NPK fertilizer production line?
Before purchasing a steam boiler for your NPK compound fertilizer production line, it’s essential to consider that the boiler’s capacity may vary depending on the formulation of the product and the process design. Different process designs can result in varying steam requirements. For instance, in a process flow utilizing round granule extrusion, a steam boiler may not be necessary. However, if you aim to produce a fertilizer formulation like 18-18-18 instead of 15-15-15, the steam requirement might increase.

