Design principle of industrial rubber conveyor belt rollers for organic NPK fertilizer/cement plant

Introduction
- This article briefly summarizes the industrial rubber conveyor belt used in fertilizer plants and cement plants, analyzes the selection principles and calculation methods of the rubber belt conveyor elevator, and selects and part designs of the belt conveyor according to the given parameter requirements based on these design criteria and calculation selection methods, and verifies the main components of the selected conveyor.
- Standard roller belt conveyor system consists of six main components: transmission device, tail and return device, middle frame, tensioning device, and belt. Finally, the installation and maintenance of the conveyor are briefly explained. At present, the belt conveyor is developing in the direction of long distance, high speed, and low friction. The air cushion/vacuum belt conveyor or so-called air slide that has appeared in recent years is one of them.
1. Introduction to tongli “Forsale” brand conveyor belt elevator
- Tongli “Forsale” band Conveyor belts and elevators are two types of machines that continuously operate transport equipment. They are mainly used to transport large quantities of bulk goods, such as ore, coal, sand, and other powders, lumps and packaged items in heavy industrial sectors such as metallurgy, mining, power, and building materials, as well as in transportation sectors.
- rubber conveyor belts are the most ideal and efficient continuous transport equipment for coal mines. Compared with other transport equipment, they not only have the advantages of long-distance, large transport capacity, and continuous transport, but also have a reliable operation and are easy to realize automation and centralized control.
- Especially for high-yield and high-efficiency mines, industrial belt conveyors have become the key equipment for the mechatronics technology and equipment of efficient coal mining. In particular, in the past 10 years, the emergence of long-distance, large-volume, and high-speed belt conveyors has further promoted their application in underground tunnels, mine surface transportation systems, open-pit mines and ore dressing plants in mine construction.

Conveyor belt/elevator Overview most up to date
What are the applications of conveyor belt elevator?
- Metal conveyor belts are a type of continuous conveyor. Continuous conveyors are one of the main types of fixed or mobile/portable conveyor belts. Their transportation characteristics are to form a continuous material flow from the loading point to the loading point and rely on the overall movement of the continuous material flow to complete the transportation of logistics from the loading point to the unloading point. In various enterprises such as industry, agriculture, and transportation, continuous conveyors are an indispensable component of the rhythmic flow line in the production process.
- Continuous fix/portable conveyor belt can be divided into:
- Conveyors with flexible traction objects, such as belt conveyors, plate conveyors, scraper conveyors, bucket conveyors, escalators, and aerial ropeways;
- Conveyors without flexible traction objects, such as screw conveyors, vibrating conveyors, etc.;
- Pipeline conveyors (fluid transportation), such as pneumatic conveying devices and hydraulic conveying pipelines.
- Among them, belt conveyors are the most widely used continuous conveyors. Belt conveyors are reliable in operation, have large conveying capacity, long conveying distances, and are easy to maintain. They are suitable for various departments such as metallurgy, coal, machinery and electricity, light industry, building materials, and grain.
What are the Classifications of industrial conveyor belts?
- There are many ways to classify fertilizer belt conveyors. According to the structure of the conveyor belts used to transport materials, they can be divided into two categories.
- One is the common belt conveyor also known as the DT-II type belt conveyor. In this type of belt conveyor, the upper belt is trough-shaped, the lower belt is flat, the conveyor belt is supported by rollers, and the outer geometric shape of the conveyor belt is flat.
- The other is the special structure belt conveyor, each with its conveying characteristics.
Development Status of chain conveyor belt:
- Chian conveyor belt elevators also known as scraper conveyors have become an important part of the combined transportation system of open-pit and underground mines. They mainly include steel rope core belt conveyors, steel rope traction belt conveyors, and continuous conveying facilities at waste dumps. These conveyors are characterized by large conveying capacity (up to 30,000t/h), wide application range (can transport ore, coal, rock, and various powdered materials, and can also transport people under certain conditions), safety and reliability, high degree of automation, easy equipment maintenance and repair, large climbing ability (up to 16°), low operating costs, and can save infrastructure investment due to shortened transportation distance.
- At present, the development trend of belt conveyors is large transport capacity, large bandwidth, large inclination, increase in single machine length and horizontal turning, reasonable use of belt tension, reduction of material transportation energy consumption, and the best way to clean the belt.
- What are the advantages of steel rope core belt conveyors:
- Applicable to ambient temperature generally °°C; in cold areas, the drive station should have heating facilities;
- It can be used for horizontal transportation, inclined upward (16°) and downward (), and can also be used for turning transportation; the transportation distance is long, and the single machine transportation can reach 15km;
- It can be laid in the open air, and the transportation line can be equipped with a protective cover or a corridor;
- The elongation rate of the conveyor belt is about 1/5 of that of ordinary belts; its service life is longer than that of ordinary belts; its troughing property is good; and the transportation distance is large.
What is the working Principle of conveyor belt? how does belt conveyor work?
- A belt conveyor is also called a belt conveyor. Its main component is a conveyor belt, also called a belt. The conveyor belt serves as a traction mechanism and load-bearing mechanism. It mainly includes the following parts: conveyor belt (usually called belt), roller and intermediate frame, roller tensioning device, braking device, cleaning device and unloading device, etc.
- The conveyor belt is wound around the transmission roller and the tail reversing roller to form an infinite ring belt. The upper and lower parts of the conveyor belt are supported on rollers. The tensioning device gives the conveyor belt the tension required for normal operation.
- When working, the transmission roller drives the conveyor belt to run through the friction between it and the conveyor belt. The material is loaded onto the conveyor belt from the loading point to form a continuous moving logistics and unloaded at the unloading point. Generally, the material is loaded onto the upper belt (load-bearing section) and unloaded on the head roller (here, the transmission roller). It can also be unloaded in the middle using a special unloading device.
The upper belt of the fuselage of the ordinary belt conveyor is supported by grooved rollers to increase the cross-sectional area of the logistics. The lower belt is the return section (empty belt without load). Generally, the lower roller is flat. Belt conveyors can be used for horizontal, inclined, and vertical transportation.
The conveyor belt is the most expensive and most easily worn component of the belt conveyor. When conveying highly abrasive materials, such as iron ore, the durability of the conveyor belt will be significantly reduced.
There are three aspects to consider to increase the traction of the transmission device:
- Increase the tension.
- Increase the wrap angle
- Increase the friction coefficient
It can be seen from the above explanation of the transmission principle that increasing the wrap angle is an effective way to increase traction.
The structure and layout of vacuum conveyor belt/air slide:
The structure of vacuum conveyor belt
- A vacuum conveyor belt is mainly composed of the following components: head frame, drive device, transmission roller, tail frame, roller, intermediate frame, tail redirection device, unloading device, cleaning device, safety protection device, etc.
Due to the structural characteristics of the belt conveyor, it has excellent performance, mainly manifested in: large transportation capacity, small working resistance, low power consumption, about 1/3 to 1/5 of the scraper conveyor; because the material moves with the conveyor, compared with the scraper conveyor, the material crushing rate is small; the single machine transportation distance of the belt conveyor can be very long. - Compared with the scraper conveyor, under the same transportation capacity and transportation distance conditions, it requires fewer equipment and fewer transfer links, saving equipment and personnel, and maintenance is relatively simple. Because the conveyor belt is costly and easy to damage, compared with other equipment, the initial investment is high and it is not suitable for conveying materials with sharp edges.
- The annual working time of the conveyor is generally 4500-5500 hours. When working in the second shift and conveying stripping materials with more conveying links, it is advisable to take the lower limit; when working in the third shift and conveying ore with fewer conveying links and there are storage bins, it is advisable to take the upper limit.
Conveyor belt transmission system how does it operate?
- The motor drives the transmission roller or other driving mechanism through the coupling and reducer, and the conveyor belt moves with the help of the friction between the roller or other driving mechanism and the conveyor belt. The driving mode of the belt conveyor can be divided into two types according to the driving device: single-point driving mode and multi-point driving mode.
- General fixed conveyor belt conveyors mostly adopt single-point driving mode, that is, the driving device is centrally installed at a certain position of the conveyor length, generally at the head of the machine. Single-point driving mode can be divided into single-roller and double-roller driving according to the number of transmission rollers.
- The drive of each roller can be divided into single-motor driving and multi-motor driving. Because the single-point driving mode is the most commonly used, any single-point driving mode that is not specified as a multi-point driving mode is a single-point driving mode, so the word “single-point” is generally omitted for the single-point driving mode.
- The single-drum and single-motor driving mode is the simplest and should be the preferred mode when considering the driving mode. Multi-motor driving is often used in large-capacity and long-distance steel rope core belt conveyors.
Design and calculation of conveyor belt elevator technical document
Known original data and working conditions:

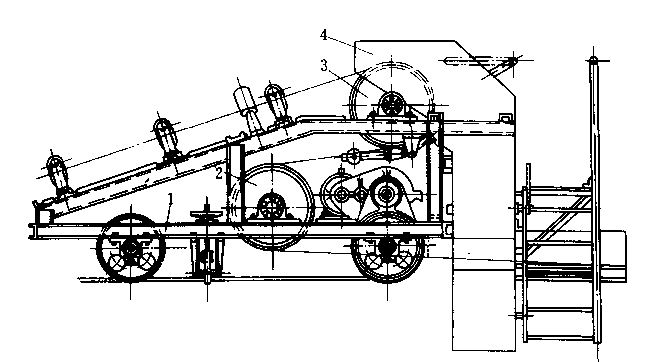
The layout of the conveyor belt elevator is preliminarily determined as shown in the figure attached:
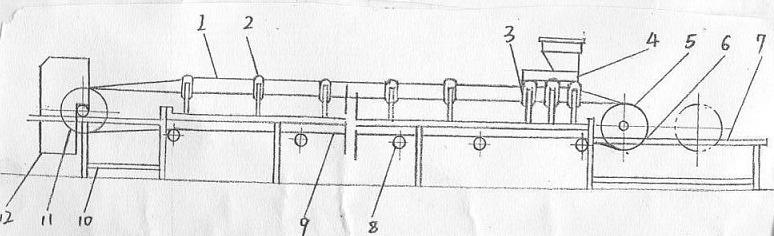
Calculation steps for “mini” type belt conveyor parts
How to determine and select the proper speed of “mini” type conveyor belt?
When selecting the “MINI” belt speed, refer to the following belt speed selection principles:
- When the conveying volume is large and the conveyor belt is wide, a higher belt speed should be selected.
- For a long horizontal MINI conveyor, a higher belt speed should be selected; the larger the conveyor angle and the shorter the conveying distance, the lower the belt speed should be.
- For materials that are easy to roll, have large particle sizes, are highly abrasive, are easy to generate dust, or have high requirements for environmental hygiene conditions, a low belt speed should be selected.
- Generally, when it is used to feed or convey a large amount of dust, the NIMI belt speed can be 0.8m/s~1m/s; or it can be determined according to the material characteristics and process requirements.
- When weighing manually, the belt speed should not be greater than 1.25m/s.
- When using a plow-type unloader, the belt speed should not exceed 2.0m/s.
- When using a discharger, the belt speed should generally not exceed 2.5m/s; when conveying fine materials or small pieces of material, the belt speed is allowed to be 3.15m/s.
- When there is a weighing scale, the belt speed should be determined according to the requirements of the automatic weighing scale.
- When conveying finished products, the belt speed is generally less than 1.25m/s. The belt speed is related to the belt width, conveying capacity, material properties, block size, and the conveyor line inclination. When the conveyor is transporting upward, the inclination is large and the belt speed should be low;
- When using a MINI conveyor belt transporting downward, the belt speed should be even lower; when transporting horizontally, a high belt speed can be selected. The determination of the belt speed should also consider the type of conveyor unloading device. When a plow-type unloading vehicle is used, the belt speed should not exceed 3.15m/s.
- The belt speed of the conveyor depends largely on the characteristics of the conveyed material, the desired conveying capacity, and the tension of the conveyor belt used.
- Powdered materials should be transported at a sufficiently low belt speed to minimize dust and Boston, especially at the loading and unloading points. Fragile materials will also limit the belt speed. When the conveyor belt and the conveyed material pass through the rollers, a lower belt speed can prevent fragile materials from jumping and breaking at the loading and unloading points.
- The conveying materials of this machine are bulk, granular, and loose materials. The belt speed is calculated to be 0.8m/s based on the required conveying volume.
How do you calculation of belt conveyor capacity for each part?
Calculation of conveying capacity for bulk materials:Q= 3600A*vρc
Actual conveying capacity Q=0.115*0.8*1.2*0.9*3600=357.7t/h
Belt elevator conveyor transmission power calculation
Drive shaft power calculation
The designed conveying length of this conveyor is 30m, and its power calculation method adopts the Japanese/european standard drive power calculation method. The calculation formula of the drive power (i.e. the drive roller shaft power) of the Japanese standard JIS B 8805-1976 power calculation method is:

P——required driving power, kW;
P₁——required driving power for no-load, kW;
P₂——required power for horizontal material transportation, kW;
P₃——required driving power for lifting materials, kW;
f——rotational friction coefficient of roller;
W——mass of moving parts other than materials, kg/m;
v——belt speed, m/min;
L——conveyor length, m;
I₀——center distance correction value, m;
H——lifting height (vertical height of rise or fall, including additional height of unloader when there is unloader), m;
Qt——conveyance, t/h;
Belt conveyor roller’s rotational friction coefficient f and center distance correction value I₀ can be obtained from the following table:
| Equipment structural features | f | I₀/m |
|---|---|---|
| Using ordinary resistance rollers, the equipment is not in good condition | 0.03 | 49 |
| Use rollers with particularly low resistance and the equipment is in good condition | 0.022 | 66 |
| Calculate the negative power operation time | 0.012 | 156 |
The mass of the moving parts excluding the material is given in the following table:
| Bandwidth/mm | 400 | 450 | 500 | 600 | 750 | 900 | 1050 | 1200 | 1400 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass W/(kg/m) | 22.4 | 28 | 30 | 35.5 | 53 | 63 | 80 | 90 | 112 |
When there is a discharger, the power Pt required by the discharger needs to be added, which is given in the following table:
| Bandwidth/mm | 400 | 450 | 500 | 600 | 750 | 900 | 1050 | 1200 | 1400 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power Pt/kW | 1.5 | 2.65 | 3.55 | 5.0 | |||||
The power of the transmission drum can be calculated from this:
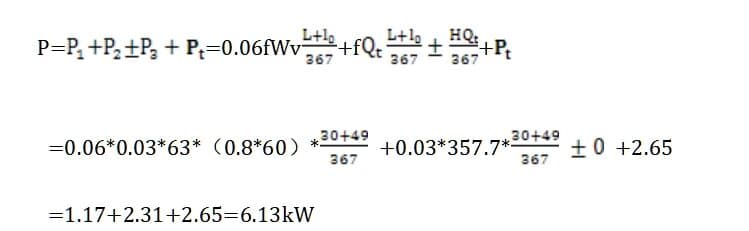
Conveyor belt tension calculation principle 2024:
The tension of the conveyor belt varies along its entire length and is affected by many factors. To ensure the normal operation of the conveyor, the tension of the conveyor belt must meet the following two conditions:
- Under any load condition, the tension acting on the conveyor belt should ensure that the circumferential force on all drive rollers is transmitted to the conveyor belt through friction, and the conveyor belt and rollers should not slip;
- The tension acting on the conveyor belt should be large enough to ensure that the sag of the conveyor belt between the two sets of rollers is less than a certain value.
Fertilizer/cement conveyor belts selection and design of drive device
- The load of the fertilizer/cement belt conveyor is a typical constant torque load, and it is inevitable to start and brake with load. The incompatibility between the starting characteristics of the motor and the starting requirements of the load is more prominent in the belt conveyor. On the one hand, in order to ensure the necessary starting torque, the current at the motor start should be 6 to 7 times larger than the current at rated operation.
- To ensure that the motor does not burn out in the fertilizer plant due to overheating due to the impact of the current, and the power grid does not excessively reduce the voltage due to the large current, this requires the motor to start as quickly as possible, that is, to increase the acceleration of the rotor so that the starting process does not exceed 3 to 5 seconds.
- The conveyor drive device is the power source of the entire belt conveyor. It consists of a motor, a coupling, a reducer, a coupling, and a transmission roller. The drive roller is composed of one or two motors that transmit torque to the transmission roller through their respective couplings, reducers, and chain couplings.
- The belt conveyor deisgn for fertilizer plant and cement plant its reducer has two-stage, three-stage and multi-stage gear reducers. The first stage is a straight bevel gear reduction transmission, and the second and third stages are helical cylindrical gear reduction transmission. There are two types of couplings connecting the motor and the reducer, one is an elastic coupling and the other is a hydraulic coupling. For this reason, there are also two types of bevel gears for the reducer; when using an elastic coupling, the first type of bevel gear is used, and the shaft head is connected with a flat key; when using a hydraulic coupling, the second type of bevel gear is used, and the shaft head is connected with a spline gear.
- The rubber conveyor transmission drum adopts a welded structure, and the main bearing adopts a self-aligning bearing. The frame of the transmission drum and the frames of the motor and reducer are all installed on a fixed large base, and the motor can be installed on either side of the head.
How to determine the correct motor power for industrial belt conveyor?
- The rated speed of the industrial motor is selected according to the requirements of the production machinery. In general, the speed of the motor is not less than 500r/min, because when the power is constant, the speed of the motor is low, the larger the size, the more expensive the price, and the lower the efficiency. If the motor speed is high, the number of pole pairs is small, the size and weight are small, and the price is also low. The total power of the motor used in this design of the industrial belt conveyor is 8kW, so a motor with a rated power of 11kW is required. It is planned to use a Y160L-6 motor, which has an efficiency of 87% and a full-load speed of 970r/min, which can meet the requirements.
How to select the best reducer/gearbox for a belt conveyor?
Overall transmission ratio
It is known that the conveyor belt width is 900. According to Table 2-77 of the “Transportation Machinery Selection and Design Manual”, the diameter D of the transmission roller is selected as 315, and the belt speed is v=0.8m/s, so the roller speed can be obtained as:
N=60v/πD=60*0.8/(3.14*0.315)=48.53r/min
The transmission ratio can be calculated as i+970/48.53=20
This design uses ZLY type reducer with a transmission ratio of 20. The nominal input is 1000r/min and the output is 50r/min.
Industrial fertilizer conveyor belts couplings design principle overview most detailed.
In the design of this drive device, couplings are widely used. Here is a brief introduction:
Couplings are commonly used components in mechanical transmission. They are used to connect two shafts together. The two shafts cannot be separated when the machine is running; the two shafts can only be separated after the machine is stopped and the connection is disassembled.
- Due to manufacturing and installation errors, deformation after bearing, and the influence of temperature changes, the two shafts connected by the coupling often cannot guarantee strict alignment, but there is a certain degree of relative displacement. This requires that when designing the coupling, various structural measures should be taken to make it have the performance of adapting to a certain range of relative displacement.
- According to whether there is compensation ability for various relative displacements (that is, whether the connection function can be maintained under the condition of relative displacement), couplings can be divided into two categories: rigid couplings (without compensation ability) and flexible couplings (with compensation ability). Flexible couplings can be divided into two categories according to whether they have elastic elements: flexible couplings without elastic elements and flexible couplings with elastic elements.
- Rigid couplings designed for fertilizer belt conveyor: This type of coupling includes sleeve type, clamp shell type and flange type. The flange coupling is a coupling that connects two flanged half couplings to transmit motion and torque. The flange coupling can be made of gray cast iron or carbon steel. Cast steel or carbon steel should be used when the coupling is overloaded or when the circumferential speed is greater than 30m/s.
- Since the flange coupling is a rigid coupling, it lacks the ability to compensate for the relative displacement of the two shafts, so the requirements for the alignment of the two shafts are very high. When there is relative displacement between the two shafts, additional loads will be caused in the machine, which will worsen the working conditions. This is its main disadvantage. However, due to its simple structure, low cost, and ability to transmit large torque, it is often used when the speed is low, there is no impact, the shaft is rigid, and the alignment is good.
- Flexible coupling: Flexible coupling without elastic elements
This type of coupling can compensate for the relative displacement of the two shafts because it is flexible. However, since there is no elastic element, it cannot buffer and reduce vibration. The following are commonly used:
Cross Slider Coupling
- The cross slider coupling consists of a half coupling with grooves on the end faces of both sides and an intermediate disk with convex teeth on both sides. Because the convex teeth can slide in the grooves, they can compensate for the relative displacement between the two shafts during installation and operation.
- The material of this coupling part can be 45 steel, and the working surface must be heat treated to increase its hardness; Q275 steel can also be used when the requirements are lower, without heat treatment. In order to reduce friction and wear, oil should be injected from the oil hole of the intermediate disk for lubrication during use.
- Because the half coupling and the intermediate disk form a moving pair and cannot rotate relative to each other, the angular velocity of the driving shaft and the driven shaft should be equal. However, when working with relative displacement between the two shafts, the intermediate disk will generate a large centrifugal force, thereby increasing the dynamic load and wear. Therefore, when selecting, it should be noted that its operating speed should not be greater than the specified value.
- This coupling is generally used for speeds, the stiffness of the shaft is large, and there is no severe impact. Efficiency, here is the friction coefficient, generally taken as 0.12~0.25;
Slider coupling
- This coupling is similar to the cross slider coupling, except that the grooves on the two half couplings are very wide, and the original middle disk is changed to a square slider without convex teeth on both sides, and is usually made of cloth-reinforced bakelite. Due to the reduced mass of the middle slider, it has a higher limit speed. The middle slider can also be made of nylon 6, and a small amount of graphite or molybdenum disulfide is added during the preparation so that it can self-lubricate during use.
- This coupling has a simple structure and compact size, and is suitable for low power, high speed and no severe impact.
Cross shaft universal coupling
- This coupling can allow a larger angle between the two shafts (the maximum angle can reach), and when the machine is running, the angle changes and can still be transmitted normally; but when it is too large, the transmission efficiency will be significantly reduced.
- The disadvantage of this coupling is that when the angular velocity of the driving shaft is constant, the angular velocity of the driven shaft is not constant, but varies within a certain range, so additional dynamic load will be generated in the transmission. In order to improve this situation, cross-axis universal couplings are often used in pairs.
This coupling has a compact structure and is easy to maintain. It is widely used in the transmission systems of automobiles, multi-head drilling machines and other machines. Small cross-axis universal couplings have been standardized and can be selected according to the standard during design. - Gear coupling: This coupling can transmit a large torque and allow a large offset. The installation accuracy requirement is not high; but the mass is large and the cost is high. It is widely used in heavy machinery.
- Roller chain coupling: The characteristics of roller chain couplings are simple structure, compact size, small mass, easy assembly and disassembly, easy maintenance, low price and certain compensation performance and buffering performance. However, due to the gap between the sleeve of the chain and its accessories, it is not suitable for reverse transmission, frequent starting or vertical shaft transmission. At the same time, it is not suitable for high-speed transmission due to the influence of centrifugal force.
Flexible coupling with elastic element
This type of coupling is equipped with elastic elements, which can not only compensate for the relative displacement between the two shafts, but also has the ability to buffer and reduce vibration. The more energy the elastic element can store, the stronger the buffering capacity of the coupling; the greater the elastic hysteresis performance of the elastic element and the friction work between the parts during elastic deformation, the better the vibration reduction capacity of the coupling.
- Elastic sleeve pin coupling: The structure of this coupling is similar to the flange coupling, except that the pin with an elastic sleeve replaces the connecting bolt. Because the torque is transmitted through the pupa-shaped elastic sleeve, it can buffer and reduce vibration. This coupling is easy to manufacture, easy to assemble and disassemble, and has a low cost, but the elastic sleeve is easy to wear and has a short life. It is suitable for connecting shafts that transmit small and medium torques with stable loads and need to be reversed or started frequently.
- Elastic pin coupling: This coupling is very similar to the elastic sleeve pin coupling, but has a large torque transmission capacity, simpler structure, convenient installation and manufacturing, good durability, and certain buffering and vibration absorption capabilities. It allows the two connected shafts to have a certain axial displacement and a small amount of radial displacement and angular displacement. It is suitable for occasions with large axial movement, frequent positive and reverse changes, and frequent starting.
- Plum blossom elastic coupling: The matching holes between the half coupling and the shaft of this coupling can be made into cylindrical or conical shapes. When assembling the coupling, the petal part of the plum blossom elastic part is clamped in the tooth side space formed by the staggered insertion of the convex teeth on the end faces of the two half couplings, so as to play a role in buffering and vibration reduction when the coupling is working.
The structural diagram of the plum blossom elastic coupling is as follows:
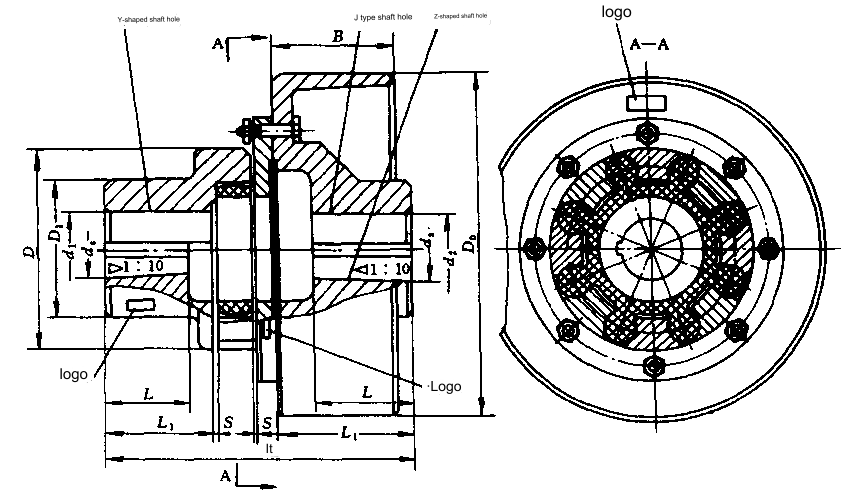
Selection of conveyor belt elevator components
Rubber belt of conveyor system:
- The conveyor belt is both a load-bearing component and a traction component in a belt conveyor (except for wire rope traction belt conveyors). It must not only have load-bearing capacity, but also have sufficient tensile strength. The conveyor belt consists of a belt core (skeleton) and a covering layer, of which the covering layer is divided into upper covering rubber, side strip rubber, and lower covering rubber.
- The belt core of the conveyor is mainly composed of various fabrics (cotton fabrics, various chemical fiber fabrics, and blended fabrics, etc.) or wire ropes. They are the backbone layer of the conveyor belt, which bears almost all the load when the conveyor belt is working. Therefore, the belt core material must have a certain strength and rigidity.
- The covering rubber is used to protect the middle belt core from mechanical damage and the influence of surrounding harmful media. The upper covering rubber layer is generally thicker. This is the load-bearing surface of the conveyor belt, which directly contacts the material and bears the impact and wear of the material.
- The lower covering rubber layer is the side of the conveyor belt that contacts the support roller, and mainly bears pressure. In order to reduce the depression resistance of the conveyor belt when it runs along the roller, the thickness of the lower covering rubber is generally thinner. The function of the side covering rubber is to protect the belt core from mechanical damage when the conveyor belt deviates and the side collides with the frame.
Drive roller conveyor belt rollers
According to the different belt core structures and materials, conveyor belts are divided into two categories: fabric core and wire rope core. The fabric core is further divided into layered fabric core and integral fabric layer core, and the materials of the fabric core include cotton, nylon, and vinyl.
- Compared with a layered fabric core conveyor belt, the integral woven fabric core conveyor belt has a smaller thickness, better flexibility, and better impact resistance under the same belt strength. It will not peel between layers during use but has higher elongation. During use, it requires a larger tensioning stroke.
- Steel rope core conveyor belt is composed of many soft thin steel wire ropes arranged at a certain distance and bonded with rubber that has good adhesion to the steel wire rope. Steel rope core conveyor belt has high longitudinal tensile strength and good bending resistance; small elongation and small tensioning strokes are required. Compared with other conveyor belts, steel rope core conveyor belt has a smaller thickness under the premise of the same belt strength.
Among steel core ropes, the quality of steel rope is one of the key factors that determine the service life of conveyor belts. It must have the following characteristics:
- It should have high breaking strength. The higher the strength of the steel core, the larger the conveyor belt can be. From another perspective, the higher the strength of the rope core, the smaller the diameter of the rope used, and the thinner the conveyor belt can be, thus achieving the purpose of reducing the size of the conveyor.
- The rope core and rubber should have high adhesion. This is of great significance for vulcanized joints. The main measures to improve the adhesion between the steel rope and rubber are to electroplate brass on the surface of the steel rope and use hard rubber.
- It should have high fatigue resistance, otherwise after the steel rope is fatigued, its adhesion with the rubber will decrease or even completely separate.
- It should have good flexibility. Pre-deformation measures are used in the manufacturing process to eliminate the residual stress in the steel rope so that the steel rope core has good flexibility and is not loose.
The upper and lower covering rubber of the conveyor belt is currently mostly natural rubber. Foreign countries use wear-resistant and weather-resistant rubber belts, such as modified rubber of tire pattern rubber as covering rubber to increase its service life. The middle of the conveyor belt uses a mixture of synthetic rubber and natural rubber.
Compared with ordinary belts, steel rope core belts have the following advantages:
- High strength: Due to its high strength, the length of a conveyor can be greatly increased. At present, the length of a domestic steel cord conveyor belt is several kilometers or even dozens of kilometers. Small elongation. The elongation of the steel cord belt is about one-tenth of that of the canvas belt, so the tensioning device has high longitudinal elasticity. In this way, the tension propagates quickly, and there will be no surge during starting and braking.
- Good troughing: Since the steel cord is arranged along the longitudinal direction of the conveyor belt and has only one layer, it fits tightly with the roller and can form a larger trough angle. In recent years, the trough angle of most steel cord conveyor belts is 35°, which can not only increase the transportation volume but also prevent the conveyor belt from running off track.
- Good impact resistance and bending fatigue resistance, and long service life: Since the steel cord is twisted into a steel cord belt core with very fine steel wire, it has very good bending fatigue and impact resistance.
- Easy to repair after damage: Once the steel cord conveyor belt is damaged, the damage will hardly expand and it is also easy to repair. On the contrary, after the canvas belt is damaged, it will peel off due to water immersion and other reasons. Reduce the strength of the canvas belt.
- Long joint life: This type of conveyor belt uses vulcanized adhesive bonding, so the joint life is very long. Experience shows that some joints have not been damaged after more than ten years of use.
- The conveyor roller is small: Since the steel rope core conveyor belt is a single-layer fine steel wire rope, the bending fatigue is slight, and the allowable roller diameter is larger than that of the canvas conveyor belt.
Steel rope core conveyor belts also have some disadvantages: - The manufacturing process requirements are high: The tension of each steel rope core must be ensured to be uniform, otherwise, the conveyor belt will deviate due to uneven tension during operation. Since there is no transverse steel rope core and canvas layer in the conveyor belt, the ability to resist longitudinal tearing must avoid longitudinal tearing.
- Easy to break wires: When the material is stuck between the roller surface and the conveyor belt, it is easy to cause the steel rope core of the conveyor belt to break. Therefore, a reliable cleaning device is required.
To facilitate manufacturing and handling, the length of the conveyor belt is generally made into 100-200 meters, so it must be connected as needed when used. There are two ways to connect rubber conveyor belts: mechanical connection and vulcanization bonding. Vulcanization bonding is further divided into hot vulcanization and cold vulcanization bonding. Plastic conveyor belts have two methods: mechanical connection and plasticization.
- Mechanical joint: Mechanical joint is a detachable joint. It damages the belt core, the joint strength efficiency is low, only 25%-60%, the service life is short, and when the joint passes through the roller surface, it damages the roller surface. It is often used on short-distance or mobile belt conveyors. The commonly used mechanical joints for fabric core conveyor belts are glued loose-leaf type, rivet fixed splint type, and hook clip type, but steel cord core conveyor belts generally do not use mechanical joints.
- Vulcanization (plasticization) joint: A vulcanization (plasticization) joint is a non-detachable joint. It has the advantages of high tensile strength, long service life, no damage to the roller surface, and a joint efficiency of up to 60%-95%, but it has the disadvantage of a complex joint process.
Functions and types of conveyor parts: transmission rollers
- The transmission roller is the main component of the transmission power. As a single-point drive method, it can be divided into single-roller drive and double-roller drive. Single-roller drive is mostly used on conveyors with low power. Double-roller drives can be used for conveyors with higher power. Its characteristics are a compact structure and increased wrap angle to increase the traction that the transmission roller can transmit. When using a double-roller drive, multiple motors can be used for separate transmission, and the gear transmission device can be used to make the two rollers run at the same speed. If the double-roller drive still does not require traction, a multi-point drive method can be used.
- The transmission roller structure of the conveyor has a steel plate welded structure and a cast steel or cast iron structure. All new design products use rolling bearings. The surface forms of transmission rollers include smooth steel rollers, cast (rubber-coated) rollers, etc.
- The main disadvantage of smooth steel rollers is that the surface friction coefficient is small, so they are generally used on short-distance conveyors with low ambient humidity. The main advantage of cast (rubber-coated) rollers is that the surface friction coefficient is large, which is suitable for conveyors with high ambient humidity and long transportation distances. Cast (rubber-coated) rollers can be divided into smooth cast (rubber-coated) rollers, herringbone groove cast (rubber-coated) rollers, and diamond cast (rubber-coated) rollers according to their surface shape.
Selection and design of conveyor parts: transmission roller
- The transmission roller is the main component for transmitting power. It is a component that drives the conveyor belt to run by the friction between it and the conveyor belt. The transmission roller is divided into three types according to the load-bearing capacity: light, medium, and heavy. The same roller diameter has several different shaft diameters and center spans for selection.
- Light: bearing aperture 80-100 mm. The shaft and the hub are single-plate welded cylinder structures with a single key connection. One-way shaft output.
- Medium: bearing aperture 120-180 mm. The shaft and the hub are connected by expansion sleeves.
- Heavy: bearing aperture 200-220 mm. The shaft and the hub are connected by expansion sleeves, and the cylinder is a cast-welded structure. There are two types of one-way shaft output and two-way shaft output.
- The transmission roller structure of the conveyor has a steel plate welding structure and a cast steel or cast iron structure. The surface forms of the drive roller include steel smooth roller, cast (rubber-coated) roller, etc. The main disadvantage of the steel smooth roller is that the surface friction coefficient is small, and it is generally used in short-distance conveyors with low ambient humidity. The main advantage of cast (rubber-coated) rollers is that the surface friction coefficient is large. They are suitable for conveyors with high humidity and long transport distances. Cast (rubber-coated) rollers can be divided into the smooth cast (rubber-coated) rollers, herringbone groove cast (rubber-coated) rollers, and diamond cast (rubber-coated) rollers according to their surface shape.
- The herringbone groove cast (rubber-coated) roller is to increase the friction coefficient. A layer of rubber with herringbone grooves is added to the surface of the steel smooth roller. This roller is directional and must not run in the reverse direction. The grooves of the herringbone groove cast (rubber-coated) roller can interrupt the water film and prevent water accumulation. At the same time, when the conveyor belt contacts the roller, the surface of the conveyor belt can be squeezed into the groove. Due to these two reasons, even if it works in a humid environment, the friction coefficient is reduced very little.
- Considering the actual situation of this design and the working environment of the conveyor: it is used for factory production, the environment is humid, the power consumption is large, and it is easy to slip, so we chose this roller. The cast rubber surface is thick and wear-resistant, and the quality is good; while the rubber coating is easy to fall off, the screw head is easy to expose, scratch the belt, and the service life is short. Compared with the two, cast rubber rollers are selected.
Industrial conveyor belts design principle of roller parts
Functions and types of conveyor roller parts:
- The roller is one of the most important components that determine the use effect of the belt conveyor, especially the service life of the conveyor belt. The structure of the roller group determines the size and nature of the load on the conveyor belt and the roller to a large extent. The basic requirements for rollers are reasonable structure, durability, good dust and water resistance of the sealing device, and reliable use. The bearings ensure good lubrication, lightweight, small rotation resistance coefficient, and low manufacturing cost, and the surface of the roller must be smooth.
- The function of the supporting roller is to support the conveyor belt and the materials on the belt, reduce the sag of the belt, ensure the smooth operation of the belt, form a trough section in the loaded branch, increase the transportation volume and prevent the leakage of materials on both sides. There are many rollers in a conveyor. The quality of the rollers has a great influence on the running resistance of the conveyor, the life of the conveyor belt, energy consumption, maintenance, and operating costs.
- The three equal-length roller groups installed on the rigid roller frame are the most common. The three rollers are generally arranged in the same plane, and the two side rollers are tilted forward by 3°; the middle roller and the side roller can also be staggered. The advantage of the latter type of roller group is that it can contact each roller, which is easy to lubricate; the disadvantage is that the roller group bracket structure is complex, and heavy, and the conveyor belt running resistance increases by about 10%. Therefore, in practice, the roller group with three rollers arranged in the same plane is mainly used.
What are the types of conveyor belt roller?
Rollers can be divided into grooved rollers, parallel rollers, buffer rollers and self-aligning rollers;
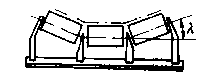
- Grooved rollers (pictured above) are used for the upper branches of belt conveyors that transport bulk materials, making the conveyor belt into a groove shape to increase the conveying capacity and prevent the material from spilling to both sides. At present, the groove angle λ of the DTⅡ series of three rollers is 35° or 45°.
- Increasing the groove angle can increase the cross-sectional area of the load and prevent the conveyor belt from deviating, but it will cause the belt to bend, which is not good for the life of the conveyor belt. To reduce the additional stress on the edge of the belt, transition rollers with groove angles of 10°, 20°, and 30° can be used between the drive drum and the first group of grooved rollers to gradually groove the belt.
- Flat rollers are composed of a straight roller and are used to transport piece goods.
Its structural diagram is as follows:
- The diameter of the roller is related to the belt width, the loose density of the material, and the belt speed. As these parameters increase, the diameter of the roller increases accordingly. The most commonly used grooved rollers for loaded branches of belt conveyors are composed of rigid, fixed-axis three-section rollers. The groove angle of a general belt conveyor is 30°.
- If the groove angle increases from 20° to 30°, the cross-sectional area of the material increases by 20% under the same bandwidth conditions, and the transportation volume can be increased by 13%. Flat rollers are often used for unloaded branches of belt conveyors. The impact of materials on the rollers at the loading point of the belt conveyor is prone to damage to the roller bearings, and buffer roller groups are often used.
- The quality of the roller sealing structure directly affects the size of the roller resistance coefficient and the life of the roller. The rotational resistance of the roller is not only related to the speed, bearings, and seals but also has a great relationship with the selection of grease. In addition to lubrication, grease also has a sealing effect.
Roller spacing - The arrangement of roller spacing should follow the principle of minimizing the deflection of the belt between the rollers. The deflection value of the belt between the rollers is generally not more than 2.5% of the roller spacing. The spacing of the upper rollers at the loading point should be smaller, generally 300-600mm and buffer rollers must be used. The spacing of the lower rollers can be 2500-3000mm or twice the spacing of the upper rollers.
- I chose a spacing of 1m between the upper rollers and 1.5m between the lower rollers. (The spacing between the upper rollers at the material connection point is 0.5m)
How to select the correct type of belt conveyor roller?
belt conveyor parts Tensioning device
- Since the belt deviation of the belt conveyor often causes equipment shutdown, material spillage, frame blockage, belt edge tearing, wear, and other faults, it seriously affects the use and life of the equipment and significantly reduces the transportation economic indicators. Therefore, attention should be paid during the design. Now we focus on analyzing the reasons for the belt deviation of the belt conveyor and propose corresponding anti-deviation measures.
- The main reasons for the belt deviation of the belt conveyor
During the operation of the belt conveyor, various eccentric forces act on the belt conveyor, causing the center of the belt to deviate from the center line of the conveyor, resulting in eccentricity. The main reasons are eccentric feeding at the unloading point, installation and manufacturing errors, wind interference, and snaking. The belt deviation can not only cause wear on the edge of the belt, material spillage, etc., but also cause waste of manpower, material resources, and financial resources. - Change the structure of the roller group to prevent the belt conveyor from deviating
The belt deviation is transmitted to the roller through the belt. The friction between the roller group and the belt changes. Therefore, to solve the problem of belt deviation in the conveyor, it is best to change the structure of the roller group. Common anti-deviation roller group structures include the forward tilting roller group, the self-aligning roller group, and the hinged hanging roller group.
- Forward tilting roller group
The difference between the forward tilting roller group and the ordinary roller group is that the side rollers on the side pillars are tilted forward at an angle along the running direction of the conveyor, generally 1.5°~2.0°. From the perspective of installation and manufacturing, it will not increase the cost. The principle of forward tilting roller group correction is: when the belt deviates, the friction between the roller on the deviated side and the belt increases, and the running direction of the belt and the linear speed direction of the roller have an angle and forward tilt angle so that the belt produces a centripetal correction force. As the forward tilt of the roller increases, the running resistance of the belt will also increase. If the conveyor uses forward tilting rollers throughout the whole process, the energy consumption will increase by about 10%~20%. Therefore, it is not suitable to use forward tilting roller groups throughout the long-distance conveyor. The side support of a reasonable forward tilt roller group should be designed to place the side rollers in two positions: forward tilt and center. During the debugging and operation process, only the rollers in the deviation section are adjusted to the forward tilt position. The energy consumption of the conveyor increases very little, not more than 3%. Under normal circumstances, the belt conveyor with stable feeding adopts a forward tilt roller group, which can better solve the problem of belt deviation. - Self-aligning roller group
The self-aligning roller group is heavy and costly. For belt conveyors with frequent changes in feeding, the self-aligning roller group has a better correction effect. The self-aligning roller groups currently used mainly include conical connecting rod type, two-way automatic self-aligning roller groups, split conical self-aligning roller groups, and self-aligning roller groups with side guard rollers. The principle of the self-aligning roller group is: that when the belt deviates, the load on the roller is redistributed and uneven, and torque is generated relative to the rotating shaft. When the deviation is small, the torque of the self-aligning roller group is less than the friction torque, and the self-aligning roller group will not rotate and will not respond to the deviation. When the deviation gradually increases and the torque exceeds the friction torque, the crossbeam rotates around the vertical axis, and as the rotation increases, the torque continues to increase, the self-aligning roller group continues to rotate, and the angle formed by the linear speed direction of the roller and the running direction of the belt increases, so that their friction force produces a centripetal component. The belt is forced to return to the center position, and it continues to move to the other side beyond the center position. The torque also gradually decreases. After several reciprocating cycles, the torque is less than the friction torque. The belt reaches stable operation. Experiments have shown that adding a self-aligning roller group for every 8 to 10 roller groups can well solve the problem of belt deviation. - Hinged hanging roller group
The rollers of the hinged hanging roller group are hinged to each other. The side rollers are hung on the frame or steel rope by a hanger that is easy to disassemble. They are particularly suitable for conveying bulk materials and for shifting conveyors that are frequently moved and have low installation accuracy. The principle of its deviation correction is: that when the belt deviates, the material deviates to one side, and the shape of the hinged roller group changes. Due to the increase in bearing capacity and friction between the belt and the roller on the side of the deviation, the inclination angle of the side roller on the side of the deviation is greater than that of the roller on the other side, causing the middle roller to deflect and generate a centering force. Since most of the material is borne by the middle roller, the total centering force is significantly increased, which has a good effect on the belt deviation correction. The advantages of the hinged hanging roller group are: First, the machine does not stop when replacing the roller. During the material conveying process, the roller group can be separated from the belt and replaced at any time, and it has strong adaptability to the load. Second, the roller group is light in weight. Since it has no crossbeam, it is much lighter than the general roller group. Third, the noise is low. Because it is a flexible connection, it can absorb vibration and impact and run smoothly. This type of roller has been widely used abroad and has also been used many times in China. However, it should be noted that the hinged hanging roller group is not suitable for underground conveyors. Because the inclination of the conveyor causes the belt to produce eccentric lateral force, the belt is not easy to make the conveyor move in the center, resulting in unstable operation.
The function of the belt tensioning device:
The function of the tensioning device is to ensure that the conveyor belt has sufficient tension at the winding end of the drive roller (i.e. the separation point between the conveyor belt and the drive roller) to generate the necessary friction between the roller and the conveyor belt to prevent the conveyor belt from slipping; to ensure that the tension of the conveyor belt is not lower than a certain value to limit the sag of the conveyor belt between the supporting rollers to avoid material spillage and increase movement resistance; to compensate for the plastic elongation of the conveyor belt during operation and the change in elastic elongation under transition conditions.
Requirements that the tensioning device should meet during use:
- When the conveyor is in normal operation, the conveyor belt has a certain constant tension at the separation point of the drive roller to prevent the conveyor belt from slipping.
- When the conveyor is started and stopped, the conveyor belt has a certain constant tension at the separation point of the drive roller. The ratio is generally 1.3 to 1.7 (it can be determined by design calculation and not less than the starting coefficient).
- Ensure that the sag of the conveyor belt at the minimum tension of the load-bearing branch and the return branch of the conveyor belt should not exceed the standard value (GB/T17119-1997 stipulates that the sag of the conveyor belt is 1/100 of the spacing between the two sets of rollers. MT/T467-1996 stipulates 1/50).
- Compensate for the plastic elongation of the conveyor belt and the change of elastic expansion and contraction under transition conditions.
- Provide the necessary tensioning stroke for the conveyor belt joint.
- During the transition of working conditions, the dynamic effect in the conveyor belt should be minimized to prevent damage to the conveyor.
Working characteristics of the tensioning device under transition conditions:
- To keep the belt tension constant at the belt separation point, an “ideal” tensioning device is generally required, which should be able to move at a large, regularly changing speed. In addition to the difficulties caused by maintaining constant tension at relatively high speeds, it is also necessary to know the law of speed change. The movement of the tensioning device is largely related to the ratio of the conveyor mass to the disassembled mass of the drive unit. As this ratio decreases, the movement speed of the tensioning device also decreases.
- The movement speed of the tensioning device decreases as the start-up time of the conveyor increases.
- For conveyors with fixed tensioning devices, the belt separation point must have a large preload to prevent the conveyor belt from slipping during startup.
- For high-power conveyors, the startup process should be extended to reduce dynamic loads and improve the working conditions of the tensioning device (reducing the stroke and its motor power).
Principles to be followed when arranging Belt conveyor tensioning devices:
The reasonable arrangement of the position of the tensioning device of the belt conveyor has a great impact on the normal operation, starting, and braking of the conveyor, as well as the design, performance, and cost of the tensioning device. In general, the arrangement of the tensioning device should follow the following principles:
- To reduce the cost of the tensioning device and minimize its tensioning force, the tensioning device is generally arranged at the place where the conveyor belt tension is the smallest as much as possible.
- For long-distance horizontal conveyors and inclined conveyors with a slope of less than 5%, the tensioning device is generally arranged on the unloaded side of the drive roller (where the tension is the smallest).
- For conveyors with shorter distances and inclined conveyors with a slope of more than 6%, the tensioning device is generally arranged at the tail of the conveyor, and the local roller of the conveyor is used as the tensioning roller as much as possible.
- The arrangement position of the tensioning device should also take into account the specific installation layout of the conveyor to make the tensioning device easy to install and maintain.
2 Types and characteristics of conveyor tensioning devices:
Spiral tensioning device
As shown in the figure, the bearing seat of the tensioning roller is installed on a sliding frame with a nut, and the sliding frame can move on the guide rail of the tail frame. It uses manpower to rotate the screw to adjust the tension of the conveyor belt. The structure of the spiral tensioning device is simple and compact, but the size of the tensioning force is not easy to grasp and cannot be kept constant during operation. It is generally used for conveyors with a length of less than 100m and low power. The tensioning stroke can be selected according to 1%-1.5% of the length.
1-screw 2-drum 3-frame 4-movable drum bearing seat
According to the DTⅡ series, the tensioning stroke is divided into three types: 500㎜, 800㎜, and 1000㎜. The maximum allowable tensioning force is shown in the table.
| Bandwidth(mm) | 500 | 650 | 800 | 1000 | 1200 | 1400 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum tension force (kN) | 9 | 16 | 24 | 38 | 54 | 75 |
Trolley weight tensioning device
The structural principle of the trolley weight tensioning device is shown in the figure. Its tensioning roller is fixed on the trolley, and the trolley is pulled by the gravity of the weight, thereby achieving the function of tensioning the conveyor belt. Its structure is also relatively simple, and it can maintain a constant tensioning force, the size of which is determined by the weight of the weight. The trolley weight tensioning device has large dimensions, occupies a large area, and has a large mass. It is suitable for conveyors with large lengths and power, especially inclined conveyors.
Trolley weight tensioning device
1-weight 2-trolley 3-pulley block 4-winch
In addition, there are straight tensioning devices and rope drum tensioning devices. For the conveyor I designed, since the belt length and transport capacity are not large, I adopted the first tensioning method, that is, the spiral tensioning device.
Conveyor belt elevator Other Parts
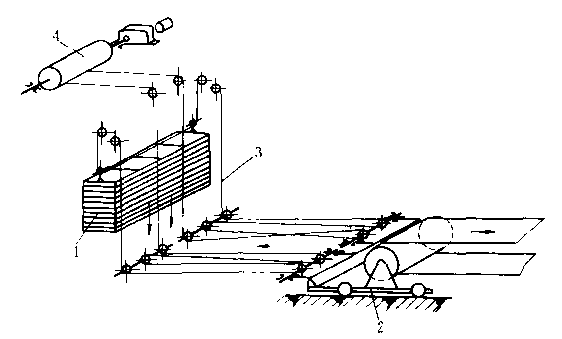
Industrial fertilizer production line conveyor belt feeding device
- Loading and transferring materials on belt conveyors is one of the most important and complex transportation operations. Studies have shown that on widely used medium-distance conveyors (within 260m in length), the service life of the conveyor belt mainly depends on whether the structure of the feeding device is reasonable.
- To reduce the wear of the conveyor belt, a series of requirements are put forward for the feeding device: the speed and direction of the material feeding to the conveyor belt should be approximately consistent with the belt speed, and the feeding should be aligned with the center of the conveyor belt to ensure that the material is evenly fed to the conveyor belt; no material accumulation and scattering is allowed at the loading point, and the logistics should be formed inside the feeding device rather than on the conveyor belt; avoid setting up baffles close to the conveyor belt behind the loading facility as much as possible, and minimize the drop of the material, especially to prevent large pieces of material from falling directly onto the conveyor belt from a high altitude.
- When the physical and mechanical properties of the conveyed material change or the use conditions change, it should be possible to adjust the material speed, and have good passing performance, especially when conveying strong viscous materials to ensure no blockage, compact structure, reliable operation, good wear resistance, etc.
- When transporting materials mixed with large pieces, the feeding device should be able to unload fine pieces and powder onto the conveyor belt to form a cushion layer first, and then load the ore to prevent large pieces of ore from directly impacting the conveyor belt. When conveying large pieces of materials with strong abrasiveness and sharp edges, the receiving section of the conveyor is preferably arranged horizontally. When the conveyor is loaded in an inclined section, the material is prone to turbulence before reaching the belt speed. To prevent material from being scattered, a high and long baffle must be set.
- The width of the feeding funnel should not be greater than 2/3 of the width of the conveyor belt. On the other hand, to prevent the funnel from being blocked, its width should be as follows: when conveying screened materials, it should not be less than 2.5 to 3 times the maximum block size, and when transporting unscreened materials, it can be taken as twice the maximum block size.
Rubber conveyor belt Discharging device
- Belt conveyors can be unloaded at the end or in the middle. The former does not require a special unloading device, while the latter can use an unloading baffle or an unloading trolley.
- The unloading baffle (plow-shaped unloader) is a straight baffle or a V-shaped baffle, which is suitable for flat belt conveyors. It can be used to unload pieces of goods or on one or both sides. The structure of the unloading baffle is very simple, but it wears the conveyor belt severely and increases the running resistance of the belt. Therefore, it is not suitable for longer conveyor belts, especially when conveying large and abrasive materials.
- For the unloading baffle to work properly, its inclination angle to the longitudinal axis of the belt must be correctly selected. The unloading trolley is installed on the horizontal section of the long belt conveyor and consists of a trolley frame, two rollers, and two guide grooves spanning both sides of the belt conveyor. The unloading trolley can move along the guide rail in the length direction of the belt conveyor. Therefore, the unloading trolley is suitable for unloading bulk materials at various unloading points in the middle of the belt conveyor. The materials are thrown out from the upper roller of the unloading trolley and unloaded from one or both sides of the belt conveyor through the guide groove.
- To guide the material flow unloading direction and reduce dust flying, a cover should be added to the unloading drum or unloading trolley. To prevent the inner surface of the cover from being overly impacted by the logistics, its shape should be made according to the trajectory of the logistics thrown out. First, the separation point between the material and the surface of the conveyor belt wrapped around the drum should be found.
Unloading trolley
1- Frame 2, 3- Guide roller 4- Material guide hopper
Mining Rubber conveyor belt Cleaning device
- During the operation of the conveyor, it is inevitable that some particles and powders will stick to the surface of the conveyor belt, which cannot be completely unloaded after passing through the unloading device. When the working surface of the conveyor belt with materials on the surface passes through the lower roller or the redirecting roller, the diameter of the conveyor belt increases due to the accumulation of materials, which aggravates the wear of the roller and the conveyor belt, causing the conveyor belt to deviate. Moreover, the continuously falling materials also pollute the site environment. Therefore, cleaning the materials adhering to the surface of the conveyor belt is of great significance to prolong the life of the conveyor belt and ensure the normal operation of the conveyor belt.
7. Electrical and safety protection devices for belt conveyor system
Safety protection devices are devices that can monitor and alarm when a fault occurs during the operation of the conveyor. They can ensure safe production and normal operation of the conveyor system, prevent damage to the mechanical parts, and protect the safety of the operators. In addition, it is also convenient for centralized control and improving the level of automation.
- The design, manufacture, transportation, and use of electrical and safety protection devices should comply with relevant national standards or professional standards, such as IEC439 “Low-voltage switchgear and control devices”; GB4720 “Electrical control equipment equipped with low-voltage electrical appliances”; GB3797 “Electrical control equipment equipped with electronic devices”.
- Protection of electrical equipment: The main circuit is required to have voltage and current instrument indicators, as well as circuit break, short circuit, overcurrent (overload), phase loss, grounding, and other protection and sound and light alarm indication. The indicator should be sensitive and reliable.
- Safety protection and monitoring: Should be selected according to the conveyor’s conveying process requirements and the operating conditions of the system or single machine. Commonly used protection and monitoring devices are as follows:
a. Conveyor belt deviation monitoring: generally installed at the head, tail, middle, and points that need to be monitored on the conveyor. When the slight deviation reaches 5% of the bandwidth, a signal is issued and an alarm is given. When the severe deviation reaches 10% of the bandwidth, a delay action is taken, an alarm is given, and the machine is shut down normally.
b. Slip monitoring: used to monitor the difference in linear speed between the drive roller and the conveyor belt, and can alarm, automatically tighten the conveyor belt, or shut down normally.
c. Overspeed monitoring: used for down-carrying or down-carrying conditions, when the belt speed reaches 115%~125% of the specified belt speed, an alarm is given and the machine is shut down urgently.
d. A pull rope switch is used for emergency shutdown along the line. A set of switches is installed every 60m on both sides of the frame along the entire length of the conveyor. After the action, it will self-lock, alarm, and shut down.
e. Other silo blockage signals, longitudinal tear signals, tensioning, braking signals, temperature measurement signals, etc. can be selected according to needs.
In conclusion
This design is mainly based on the existing design standards for profiling design, and the design and calculation are strictly carried out according to the design standards and relevant specifications.
The main achievements of the design are:
- The structure, principle, and function of each part of the conveyor are mastered proficiently, and the development status at home and abroad is understood.
- The problems that often occur during the use of the conveyor are mastered, and appropriate solutions are made for each problem in the design.
- The whole process of mechanical (machine, equipment) design is systematically mastered. It is understood that the acquisition of each parameter requires a lot of calculation and demonstration.
The main problems:
- The structural dimensions and installation dimensions of some parts are not accurately grasped.
- Some old parts are also used in the design.
- The calculation of some parameters is not accurate enough. The connecting plate design has some flaws.
Suggestions for further research:
- Simplify the overall conveyor according to the actual situation to reduce the weight and volume of the conveyor.
- Optimize the design of each component to optimize the function of each part.

