Improving Agglomerates through Coating
Coating as a surface treatment technology is widely used in various industries dealing with agglomerate structure to achieve a variety of goals. By coating specific materials on the surface of particles, granules, or other agglomerates, coatings can enhance the properties of a product, such as minerals, chemicals, etc. Coatings not only maintain the integrity of the product, but also mitigate issues such as dirt and abrasion and even improve product performance. This article will look at the benefits of coatings, how the coating process works, and the factors to consider when selecting an appropriate coating.

Key benefits of coatings
Reducing dust and wear
Dust not only causes environmental pollution, it can also lead to product loss. Coatings create a protective barrier on the surface of the particles, effectively reducing the generation of dust and fines. This is particularly common in the fertilizer industry, where coatings improve product stability during transportation and use.
Prevents agglomeration and moisture absorption
Coatings prevent the formation of crystalline structures between particles, thus reducing caking and maintaining product integrity. At the same time, a variety of oils, waxes, clays, polymers and other coating materials prevent moisture absorption, which is particularly important for moisture-absorbent fertilizers such as urea and potassium chloride.
Improved flowability
Coatings can adjust the surface properties of particles and reduce the angle of repose, thereby improving the flowability of the material. This helps to improve product conveyance and handling in production facilities, such as unloading from train cars and transferring between conveyor belts.
Enhancing Appearance
Coatings can give pellets a smooth, shiny surface that enhances the marketability of the product. In addition, coatings can be used to color granules, such as colored granules for roofing asphalt shingles.
Improve Product Performance
Coatings can affect the solubility of a product or control its release characteristics, which is common in the fertilizer industry. Some coatings can also be used as carriers to add additional functional ingredients, such as a clay coating to promote clumping in cat litter.

Coating Options
A wide range of coating types are available, including mineral oils, clays, waxes, polymers, latexes, silicates, and more. In some cases, multiple coatings or combinations of coatings may be required to achieve the desired results.
Many factors need to be considered when selecting a coating for a particular application. Below are some of the most critical factors to consider in coating selection:
Industry and Application
Similar to adhesive selection, the industry and/or end use of the product may determine the most appropriate type of coating. For example, a coating that may be toxic to the soil would not be appropriate for a fertilizer product, whereas a plant-derived coating would be an effective coating and may also add value to the product.
Cost
As with any other program consideration, cost is often a major factor in coating selection. Some coatings may offer a high performance solution, but are too costly to be practical. This is of particular concern in industries where margins are slim.
Ease of use
Ease of use is also an important consideration. Some materials are easy to apply and distribute in the material bed (e.g., oils, waxes, some polymers and latexes). The contact action of particles tumbling and colliding in the drum helps to deliver the coating evenly to all particles.
Conversely, other coatings may be effective in theory, but challenging and costly to apply. This typically occurs with materials such as hot melts, dyes and acids, which do not spread readily on contact. These difficult-to-coat materials may require specially designed spray systems to ensure uniform coating distribution.
Coating process
The coating process utilizes two main types of equipment: the coating drum and the pugmill mixer. Both machines have their own characteristics and are designed to achieve a uniform coating of the particles.
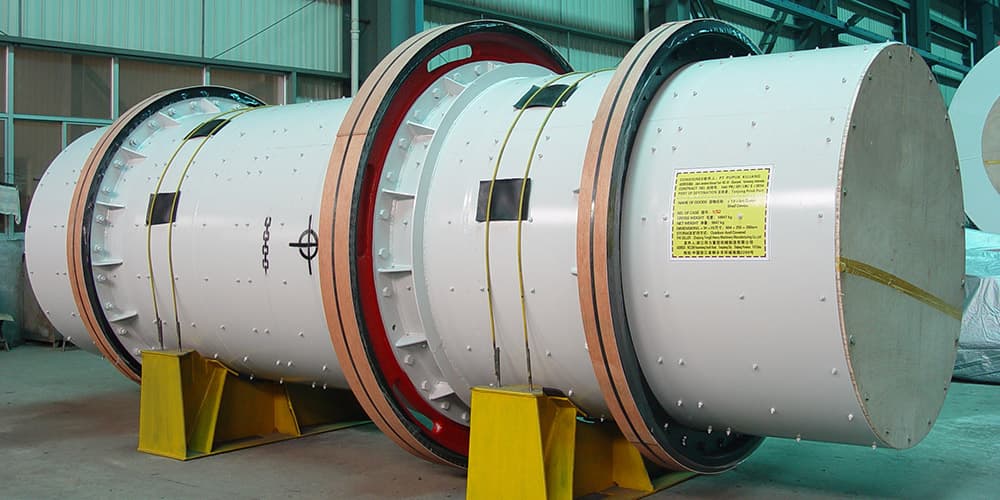
Coating drums
Coating drums are industrial machines used to apply a uniform coat of material to particles. The material to be coated is loaded into the drum, along with the coating material. As the drum rotates, the particles are tumbled and As the drum rotates, the particles are tumbled and mixed, ensuring that they are evenly coated.

pugmill mixers
Pugmill mixers, also known as paddle mixers or pug mills, can have a capacity ranging from 500 lb/hr to 250 TPH. The capacity of a pugmill mixer is generally The capacity of a pugmill mixer is generally related to the width of its trough, with wider troughs having higher capacities. Pugmills are horizontal, continuous mixers that combine solid and liquid feed components into a homogeneous mixture.
Factors to Consider When Applying Coating Equipment in Fertilizer Production Lines
Selecting the right coating equipment for a fertilizer production line is an important decision that requires a number of factors to be considered. The following are key considerations in selecting fertilizer coating equipment.
- Particle size and shape: Particle size and shape will affect the choice of coating equipment. For smaller particles, smaller coating equipment is needed to ensure a uniform coating. For irregularly shaped particles, coating equipment that provides good mixing results is required.
- Coating material: The nature of the coating material influences the choice of coating equipment. Coating materials with high viscosity require a coating equipment that provides powerful mixing. Coating materials with high volatility require coating equipment that prevents loss of coating material.
- Required Coating Thickness: The required coating thickness affects the choice of coating equipment. For thicker coatings, coating equipment that provides multiple layers of coating is required. For thinner coatings, coating equipment that provides precise control is required.
- Productivity: Productivity affects the choice of coating equipment. For high productivity applications, coating equipment that can handle large quantities of particles quickly is required. For low productivity applications, smaller coating equipment can be used.
Coating technology offers a multifaceted solution for improving agglomerate structure. Through careful selection of coating materials and optimization of process parameters, product quality, performance and market competitiveness can be significantly improved. Given the complexity of coating applications, small-scale trials and testing are essential to determine the best coating solution.
When selecting a coating, a number of factors such as industry requirements, cost-effectiveness, application difficulty and product characteristics need to be taken into account in order to achieve optimum agglomerate structure improvement.

