Rise in Anaerobic Digestion Boosts Manure Granulation
In recent years, anaerobic digestion technology has become increasingly popular for food waste treatment and on-farm applications and is driving a shift towards a circular economy model of food production. This trend is particularly evident in poultry and livestock production, where opportunities for manure pelletization have been significantly enhanced through the use of anaerobic digesters.

Historical evolution of the application of anaerobic digestion
In the 1970s, renewable energy incentives drove the adoption of anaerobic digestion on farms that sold captured energy to the grid at a discounted rate. However, as the incentives were eliminated, the economic viability of the practice declined. Now, as the demand for “green” natural gas grows, farms are turning to anaerobic digestion again. In this method, farmers can capture methane emissions and inject them into natural gas pipelines, where they can be converted into a variety of value-added products.
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, the number of manure-based anaerobic digesters in the U.S. has grown steadily over the past 20 years, from 25 in 2000 to nearly 350 by 2023. This growth is due in part to the trend toward industrialized farms, as well as state and federal incentives implemented in 2011 to limit methane emissions.
Digestate Processing: Pelletization Boosts Value
While the primary purpose of anaerobic digestion at most facilities is to obtain biogas, the solids that remain after digestion are also valuable. The digestion process concentrates nutrients and converts them into a form that is more readily absorbed by the plant, making these solids an upgraded source of nutrients that are more valuable for reuse.
By pelletizing digestate into a dry fertilizer product, farmers can eliminate waste management challenges, significantly increase the value and marketability of their products, and create an additional source of income while achieving more sustainable operations and reducing their carbon footprint.
Digestate Pelletization Process
The Digestate Pelletization process typically consists of the following key steps.
Solid-liquid separation
The digested slurry is first separated into a solid-liquid separation, resulting in a “nutrient cake” (solid fraction) and a “tea” (liquid fraction). This step is essential because.
- The separated solid fraction (nutrient cake) is the raw material for subsequent granulation.
- The moisture content of the solids is kept within a suitable range to facilitate subsequent processing.
- The liquid fraction can be used as a liquid fertilizer
Pretreatment
The separated solids are subjected to the necessary pre-treatment, including
- Grinding: to ensure uniform particle size
- Screening: to remove impurities such as coarse fibers, sand, etc.
- Moisture adjustment: If the solids are too wet, they can be dried moderately.
Mixing and particle formation
Mixing and granule formation in a mixer.
- The wet material is mixed with the dry recycled material in the right proportions.
- The kneading action of the mixer results in a homogeneous mixing of the materials and the formation of the initial granules.
- Binders or other useful additives can be added.
Drying, sieving and cooling
- Drying of the granules in a rotary dryer or fluidized bed dryer.
- Sieving to obtain particles of the right size
- Recycling of oversized pellets by crushing after sieving
- Cooling of the finished pellets to improve storage stability.
This process converts digested solids into a dry, uniform, granular fertilizer product that is easy to store and transport, significantly increasing its value and marketability. By carefully controlling each step of the process, it is possible to ensure that the final product is of consistent quality and meets the needs of agricultural applications.
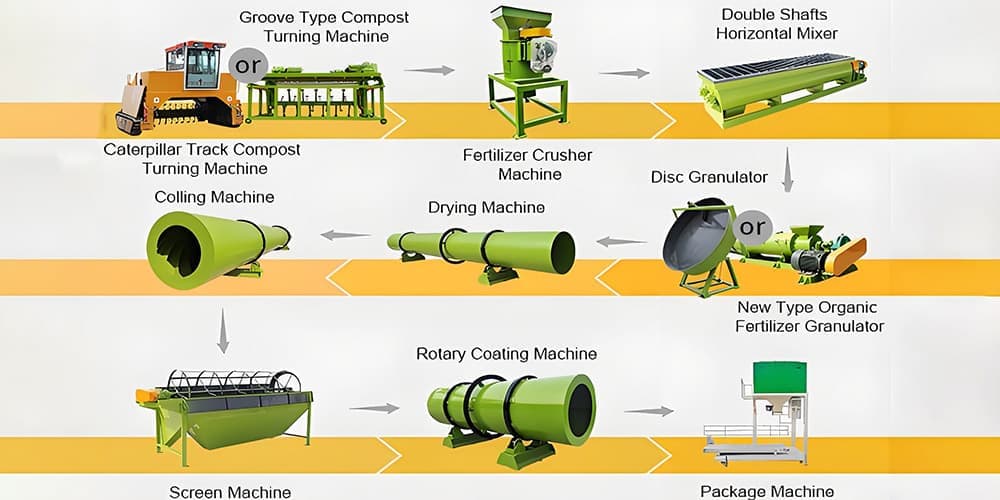
How to ensure the quality of the solid granulation process after anaerobic digestion?
There are several key steps that can be taken to ensure the quality of the solids pelletization process after anaerobic digestion.
Optimize the solid-liquid separation process
Solid-liquid separation is the basis for granulation. Efficient separation equipment, such as screw presses or centrifuges, should be selected to obtain a “nutrient cake” with a moderate moisture content. Control the moisture content of separated solids between 60-70%, which can ensure the moisture required for subsequent processing, but will not be too wet to affect the granularity.
Strict control of pretreatment
Necessary pre-treatment of the separated solids includes.
- Grinding: to ensure uniform particle size for subsequent molding.
- Screening: to remove impurities such as coarse fibers and sand.
- Moisture adjustment: If the solids are too wet, they can be dried moderately.
Precise proportioning and mixing
In the mixer, the wet material is mixed with the dry recycled material in the right proportion. Typically, the ratio of dry material to wet material is between 1:1 and 2:1, depending on the characteristics of the raw material. Make sure that the mix is homogeneous and that agglomerates are not formed.
Optimize pellet forming conditions
Control the operating parameters of the mixer, such as speed, residence time, etc., in order to obtain the ideal particle shape. Consider adding appropriate amount of binder to improve the strength of granules.
Fine control of drying process
Choose suitable drying equipment (e.g. rotary dryer or fluidized bed dryer) and strictly control the drying temperature and time. Too high a temperature may lead to nutrient loss, while too low a temperature may affect product storability. The moisture content of the final product is usually kept at 10-15%.

Strict sieving and cooling
Use multi-stage screens to ensure uniform particle size. Any oversized particles are crushed and recycled. Cooling is also important to prevent agglomeration and improve storage stability.
Establishment of a quality control system
Regularly test the physical and chemical indicators of the product, such as moisture, nutrient content, particle strength, etc.. Establish a comprehensive quality traceability system to ensure that the quality of each batch can be controlled.
Continuous optimization of process parameters
According to the characteristics of different raw materials and seasonal changes, continuously adjust the process parameters, such as mixing ratio, drying temperature, etc., in order to maintain stable product quality.
Through the above measures, the quality of the solid granulation process after anaerobic digestion can be effectively ensured, and high-quality and stable fertilizer products can be produced. This not only improves the market value of the product, but also creates an additional source of income for the farm and promotes the development of agricultural circular economy.

Conclusion:
Anaerobic digestion technology and manure pelletization are key tools for realizing a circular economy in agriculture. They can help farms increase productivity, reduce waste emissions and protect the environment.
TONGLI, as an industry leader, is committed to providing professional post-digested solids processing solutions to help farms convert post-digested solids into high-quality fertilizer products and high-quality bedding used in dairy farms, which realizes the recycling of resources and contributes to the sustainable development of agriculture.
With our rich experience and professional technical team, we can provide customers with one-stop service from process development and testing, plant engineering to equipment design and manufacturing, as well as providing complete parts and service support.
If you would like to learn more about converting manure digested solids into fertilizer products, bedding or both, please contact us! We will be happy to assist you.

